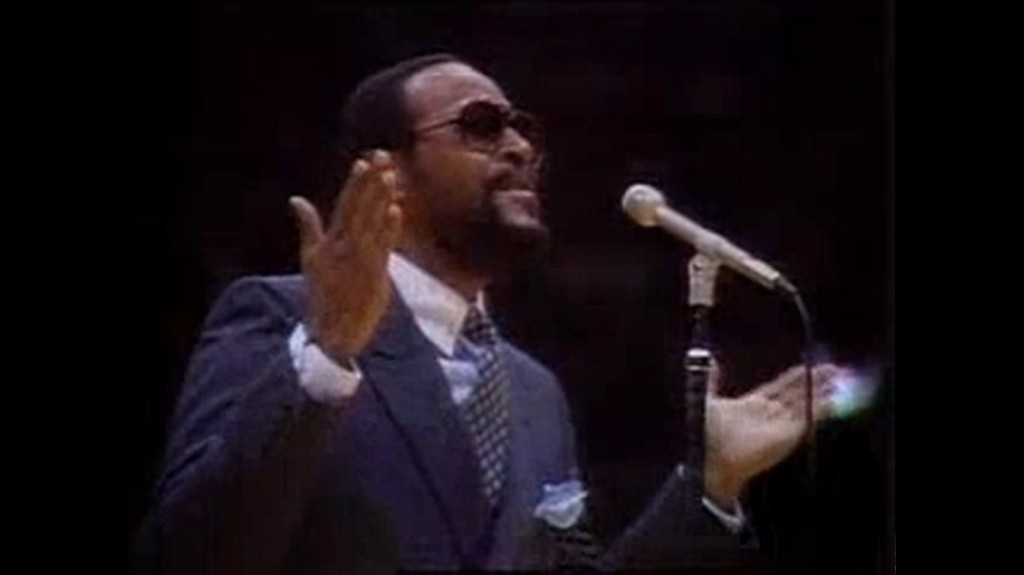
Diana Ross – Actress, singer

Diana Ross was born in Detroit, Michigan on March 26, 1944. The second-eldest child of Ernestine (née Moten) (January 27, 1916 – October 9, 1984), a schoolteacher, and Fred Ross, Sr. (July 4, 1920 – November 21, 2007), a former United States Army soldier, Ross would later say that she didn’t see much of her father until he had returned from service following World War II.
Ross and her family originally lived at Belmont Road in the North End section of Detroit, near Highland Park, Michigan, where she was neighbors with Smokey Robinson, who first met Ross when she was eight. Despite her early life as a “tomboy”, upon her teenage years, Ross had dreams of being a fashion designer. She studied design, millinery, pattern-making and seamstress skills while attending Cass Technical High School, a four-year college preparatory magnet school, in downtown Detroit. In her late teens, Ross worked at Hudson’s Department Store where, it was claimed in biographies, that she was the first black employee “allowed outside the kitchen”. Ross graduated in January 1962, one semester earlier than her classmates. Around this same time, Ross was turned on by the emerging rock and roll music scene, and her early influences included Frankie Lymon and Etta James.
At fifteen, Ross was brought to the attention of music impresario Milton Jenkins, manager of the local doo-wop group the Primes, by Mary Wilson. Paul Williams, then member of The Primes, convinced Jenkins to include Ross in the Primettes, considered a “sister group” of the Primes. Ross was part of a lineup that included Wilson,Florence Ballard and Betty McGlown, who completed the lineup. In 1960, following their win at a singing contest in Windsor, Ontario, Canada, the group auditioned for a spot on Motown Records after Smokey Robinson introduced the young group to Berry Gordy. Upon learning of their ages, Gordy advised them to come back after graduation. Undeterred, the quartet stayed around Motown’s Hitsville U.S.A. headquarters, offering to provide extra help for Motown’s recordings, often including hand-claps and background vocals.
In January 1961, Berry Gordy agreed to sign the young act under the condition they change their name. Each member picked out various names from friends. Eventually they settled on The Supremes, though Ross initially had apprehensions toward the name – she felt the name would mistake them for a male vocal group. But Gordy agreed with the new name and signed them on January 15 of that year. During the group’s early years, there was no designated lead vocalist for the group as they had agreed to split lead vocals between their choice of song material; Ross favoring the uptempo pop songs. That changed in 1963 when Gordy assigned Ross, who had already sung lead on the majority of their early singles, as the main lead vocalist, considering that her vocals had potential to reach Gordy’s dreams of crossover success. Between August 1964 and May 1967, Ross, Wilson and Ballard sang on ten number-one hit singles, all of which also made the UK top forty. The group had also become a hit with audiences both domestically and abroad, going on to become Motown’s most successful vocal act throughout the sixties.
In 1968, Ross started performing as a solo artist mainly on television specials, including The Supremes’ own specials such as TCB and G.I.T. on Broadway. In mid-1969, Gordy decided to have Ross leave the group by the end of the year and Ross began sessions for her own solo work that July. One of the first plans for Ross to establish her own solo career was to bring in a new Motown recording act. Though she herself didn’t claim discovery, Motown pinned Ross as having discovered The Jackson 5. In November, Ross confirmed a split from the Supremes on Billboard. Ross’ presumed first solo recording, “Someday We’ll Be Together”, was eventually released as a Supremes recording and became the group’s final number-one hit on the Hot 100. Ross made her final appearance with the Supremes at the Frontier Hotel in Las Vegas on January 14, 1970.
After her obligations with the Supremes were fulfilled, Ross signed a new contract as a solo artist in March 1970. Two months later, Motown released her eponymous solo debut, which included the hits, “Reach Out and Touch (Somebody’s Hand)” and “Ain’t No Mountain High Enough,” the latter song becoming her first number-one single as a solo artist on the pop and R&B charts, also becoming an international hit reaching the UK top ten, and winning Ross her first Grammy nomination. Ross only released one solo recording in 1972. She reemerged in 1973 with “Touch Me in the Morning,” which became her first single to reach number-one in three years. The album of the same name became Ross’s first non-soundtrack studio album to reach the top ten, peaking at #5. Later that year, the Diana & Marvin album, her duet album with Gaye, was released, and spawned five hit singles, including three released in the United States and two in Europe, gaining an international hit with their cover of The Stylistics’ “You Are Everything.” In 1973, Ross began giving out concerts overseas where she immediately sold out at every concert venue she performed at. That year, Ross became the first entertainer in Japan’s history to receive an invitation to the Imperial Palace for a private audience with the Empress Nagako, wife of Emperor Hirohito.
Ross’s follow-up albums, 1977’s Baby It’s Me and 1978’s Ross, however, both faltered on the charts, mainly due to lack of promotion and a period of growing tension between Ross and Gordy, stemming from an incident in 1975 after Ross struck him after the two engaged in an argument on the set of Ross’s film, Mahogany. In 1977, Ross starred in her own one-woman show at Broadway, titled An Evening with Diana Ross. Her performance later resulted in her winning a Tony Award.
After catching the group Chic at a concert where she attended with her daughters, Ross advised to the leaders of the band, Nile Rodgers and Bernard Edwards to work with them in New York on her next album. They agreed and, in 1980, Ross released the Diana album. The album became her highest-charting solo album and her most successful, featuring hits including the number-one hit, “Upside Down,” her first song to reach the top position in four years. Another song, “I’m Coming Out,” became equally successful; its hook would later be sampled for “Mo’ Money, Mo’ Problems.” Diana would become Ross’s final studio album under her Motown contract. She would later work on four songs to complete her contractual obligations for the compilation album, To Love Again, which would be released in May 1981. Though Ross had sought to leave Motown in 1980 shortly after the release of Diana, she discovered, just as she was planning to leave Motown, that she only had up to $150,000 in her name despite helping Motown to earn millions of dollars with her recordings in the twenty years she had been signed to the label. Ross signed with RCA on May 20, 1981, and her $20 million deal in 1981 became then the most lucrative contract of any recording artist at the time. After leaving, Ross achieved her sixth and final number-one hit with Lionel Richie on the ballad “Endless Love” around the same time Ross left the label.
In 1971, Diana Ross began working on her first film, Lady Sings the Blues, which was a loosely based biography on music legend Billie Holiday. Some critics lambasted the idea of the singer playing Holiday considering how “miles apart” their styles were. At one point, Ross began talking with several of Holiday’s acquaintances and listened to her recordings to get into character. During an audition to acquire the role, Ross would act on cue to the film’s producers’s commands, helping Ross to win her part. When Berry Gordy heard Ross perform covers of Holiday’s material, he felt Ross had put “a little too much” Holiday in her vocal range, advising Ross to “put a little Diana back into it.”
Ross also talked with doctors at drug clinics in research of the film, as Holiday had been a known drug addict. Ross would later make a crucial decision when it came to interpreting Holiday’s music: instead of flatly imitating Holiday, she only focused on Holiday’s vocal phrasing. “Lady Sings the Blues” opened in theaters in October 1972, becoming a major success in Ross’s career. Ross’s role in the film won her Golden Globe Award and Academy Award nominations for Best Actress. Alongside Cicely Tyson, who was nominated for her role in the film, Sounder, they were the first Black actresses to be nominated for the Academy Award for Best Actress since Dorothy Dandridge. The soundtrack to “Lady Sings the Blues” became just as successful, reaching #1 on the Billboard 200 staying there for two weeks and breaking then-industry records by shipping 300,000 copies during the first eight days of its release. At nearly two million in sales, it is one of Ross’s best-selling albums to date.
After the film, Ross returned to her music career, reemerging with another film in 1975 with Mahogany, her second film, in which she starred alongside Billy Dee Williams and whose costumes she designed. The story of an aspiring fashion designer who becomes a runway model and the toast of the industry, Mahogany was a troubled production from its inception. The film’s original director, Tony Richardson, was fired during production, and Berry Gordy assumed the director’s chair himself. In addition, Gordy and Ross clashed during filming, with Ross leaving the production before shooting was completed, forcing Gordy to use secretary Edna Anderson as a body double for Ross. While a box office success, the film was not well received by the critics: Time magazine’s review of the film chastised Gordy for “squandering one of America’s most natural resources: Diana Ross.”
In 1977, Motown acquired the film rights to the Broadway play The Wiz, an African-American reinterpretation of L. Frank Baum’s The Wonderful Wizard of Oz. The film initially was to include the stage actors who had performed on the play. However, the role of Dorothy, which had been performed onstage by Stephanie Mills, would be given to Ross after she convinced film producer Rob Cohen to cast her in the role of Dorothy. This decision eventually led to a change in the film’s script in which Dorothy went from a schoolgirl to a schoolteacher. The role of the Scarecrow, also performed by someone else onstage, was eventually given to Ross’s former Motown label mate, Michael Jackson. The film adaptation of The Wiz had been a $24 million production, but upon its October 1978 release, it earned only $21,049,053 at the box office. Though pre-release television broadcast rights had been sold to CBS for over $10 million, the film produced a net loss of $10.4 million for Motown and Universal. At the time, it was the most expensive film musical ever made. The film’s failure ended Ross’s short career on the big screen and contributed to the Hollywood studios’s reluctance to produce the all-black film projects which had become popular during the blaxploitation era of the early to mid-1970s for several years. The Wiz was Ross’s final film for Motown.
Ross had success with movie-themed songs. While her version of Holiday’s “Good Morning Heartache” only performed modestly well in early 1973, her recording of “Theme from Mahogany (Do You Know Where You’re Going To)” gave Ross her third number-one hit, in late 1975. Three years later, Ross and Michael Jackson had a modest dance hit with their recording of “Ease on Down the Road.” Their second duet, actually as part of the ensemble of The Wiz, “Brand New Day,” found some success overseas. Ross scored a Top 10 hit in late 1980 with the theme song to the 1980 film It’s My Turn. The following year, she collaborated with former Commodores singer-songwriter Lionel Richie on the theme song for the film Endless Love. The Academy Award-nominated title single became her final hit on Motown Records, and the number one record of the year. Several years later, in 1988, Ross recorded the theme song to The Land Before Time. “If We Hold On Together” became an international hit, reaching number-one in Japan.
In 1984, Ross’s career spiked yet again with the release of the million-selling Swept Away. This featured a duet with Julio Iglesias, “All Of You,” which was featured on both the albums they had then released—his 1100 Bel Air Place as well as her Swept Away. It and the title selection both became international hits, as did the chart-topping ballad, “Missing You,” which was a tribute to Marvin Gaye, who had died earlier that year. Her 1985 album, Eaten Alive, found major success overseas with the title track and “Chain Reaction,” although neither of the songs became the best-sellers she was once accustomed to in America. Earlier in 1985, she appeared as part of the supergroup USA for Africa on the ‘”We Are the World“‘ charity single, which sold over 20 million copies worldwide. Ross’s 1987 follow up to Eaten Alive, Red Hot Rhythm & Blues, found less success than the prior album. In 1988, Ross chose to not renew her RCA contract. Around this same time, Ross had been in talks with her former mentor Berry Gordy to return to Motown. When she learned of Gordy’s plans to sell Motown, Ross tried advising him against the decision though he sold it to MCA Records in 1988. Following this decision, Gordy offered Ross a new contract to return to Motown with the condition that she have shares in the company as a part-owner. Ross accepted the offer.
Despite its heavy promotion, Diana’s next album, Workin’ Overtime, was a critical and commercial failure. Subsequent follow-ups such as The Force Behind the Power(1991), Take Me Higher (1995), and Every Day Is a New Day (1999) produced similarly disappointing sales. Ross had more success overseas with the albums than she did in America. In 1994, Ross performed at the opening ceremony of the FIFA World Cup, hosted in the USA. Her performance has become a running joke in football circles due to her obvious miming and for missing the goal from close range. On January 28, 1996, Ross performed the Halftime Show at Super Bowl XXX.
In 1999, she was named the most successful female singer in the history of the United Kingdom charts, based upon a tally of her career hits. Madonna would eventually succeed Ross as the most successful female artist in the UK.
In 2004, after spending several years away from the spotlight and after a stint in jail for committing a DUI, Ross returned to live touring, first in Europe and then in the United States all within the same year. In 2005, she participated in Rod Stewart‘s Thanks for the Memory: The Great American Songbook, Volume IV recording a duet version of the Gershwin standard, “I’ve Got a Crush on You“. The song was released as promotion for the album and later reached number 19 on the Billboard’s Hot Adult Contemporary chart, marking her first Billboard chart entry since 2000. Ross was featured in another hit duet, this time with Westlife, on a cover of Ross’ 1991 hit, “When You Tell Me You Love Me”, which repeated the same chart success of the original just fourteen years before.
In June 2006, Universal released Ross’ shelved 1972 Blue album. It peaked at #2 on Billboard’s jazz albums chart. Later in 2006, Ross released her first studio album in seven years with I Love You. It would be released on EMI/Manhattan Records in the United States in January 2007. EMI Inside later reported the album had sold more than 622,000 copies worldwide. Ross later ventured on a world tour to promote I Love You which garnered rave reviews. In 2007, she was honored twice, first with the Lifetime Achievement Award at the BET Awards and later was one of the honorees at the Kennedy Center Honors.
In 2010, Ross embarked on her first headlining tour in three years titled the More Today Than Yesterday: The Greatest Hits Tour. She dedicated the entire concert tour to her late friend, Michael Jackson, who died in June 2009. Ross has garnered critical success as well as commercial success from the now two-year tour. In February 2012, Diana Ross received her first ever Grammy Award, for Lifetime Achievement, and announced the nominees for the Album of the Year. In May, a DVD of Ross’ Central Park concert performances, “For One & For All”, was released and featured commentary from Steve Binder, who directed the special.